With the rise in use of QR codes on products and packaging, brands have begun turning to serialized QR codes for their unique ability to address key business challenges and opportunities. From marketing to supply chain traceability and even packaging compliance, serialized QR codes offer benefits to global brands that other SKU or batch-level codes simply cannot. This guide explains what serialized QR codes are, how they’re used by global product companies, and how brands can successfully adopt them. The information is based on our experience with global rollouts of serialized QR codes for many use cases and across a wide variety of industries.
Serialized QR Codes: Everything a brand should know
Serialized QR codes are becoming increasingly popular as brands seek to drive more value from their packaging.

Introduction
What is a serialized QR code?
A serialized QR code is one that unique to each product. The uniqueness is made possible by a unique number or string in the URL embedded in the QR code. That number or string is associated to the unique product in one or more systems or databases, such as an ERP.
“Serialization” is the industry term for the technical process used to accomplish the high-volume, zero-conflict generation of random unique identifiers for use in serialized QR codes. While many systems, including ERPs can generate serialized QR codes, some such as Scantrust’s enterprise QR code generator is specifically built for both generating and managing those codes at scale and specifically for use on products and product packaging.
Why are brands shifting to serialized codes?
There are increasing use cases for serialized codes and meanwhile, the costs to implement them are going down:
- Cost are coming down due to the rise of more accessible digital or hybrid printing. This type of variable data printing (VDP) is required for serialization.
- Many products now require batch or unit-level traceability for compliance reasons, for example tobacco and pharmaceutical products.
- Digital Product Passports will be required on many products sold in the E.U.
- The rise of e-commerce and new online sales channels has led to a rise in product diversion and counterfeiting problems. Several industries use serialized QR codes to successfully address these problems.
- Brands have discovered how to leverage unique QR codes on products for marketing campaigns, especially loyalty programs.
How do you generate serialized QR codes?
Enterprise QR code generators generate serialized QR codes in a few different ways:
- Using programmatic interfaces/API
- With web-based tools that offer required files downloading
- Via printing work orders that integrate the QR code generator directly with printing equipment
How do you create QR codes with serial numbers?
QR codes with serial numbers can be achieved through software integration, such as with an enterprise QR code solution or generator. When the QR codes are generated, they are associated with serial numbers, or they are scanned and associated with them at some later point in the manufacturing, production, or labeling process.
What are the use cases for serialized codes?
Serialization projects frequently begin with cross-departmental initiatives, from shared budgets, due to their broad benefits. Below, we’ve listed a few of the use cases that we’ve seen companies succeed with the most.
Supply chain traceability use cases for serialized codes
Serialized QR codes provide the ability to do unit-level track-and-trace, showing how products reach market. Specific traceability use cases include:
- Detect product diversion, parallel imports, and grey market sales
- Inventory management
- Measure stock aging by distributor
- Tracking unit or batch quality issues
- Managing recalls
Marketing, sales, and support use cases for serialized codes
- Loyalty and rewards programs
- Anti-counterfeiting
- Warranty management
Compliance use cases for serialized codes
Digital Product Passports (DPPs) – New E.U. laws will require trillions of products sold in the E.U. to carry QR codes or other digital identifiers associated with so-called DPPs stating where and how the product was made, where and how the packaging was made, and where and how to recycle or upcycle the items. Many companies are getting ahead of the requirements for their industry, even though the Circular Economy Action Plan is implementing requirements across industries in a staggered timeline. For large brands, compliance will take years across thousands of stock keeping units/SKUs, and as such, many brands are actively planning or already implementing a DPP compliance plan. For some product categories, batch-level codes will suffice, but for others, unit-level will be required. It will take time to implement so there’s no better time to begin than now.
Case study: Motul uses QR codes on products for marketing, anti-counterfeiting, and more
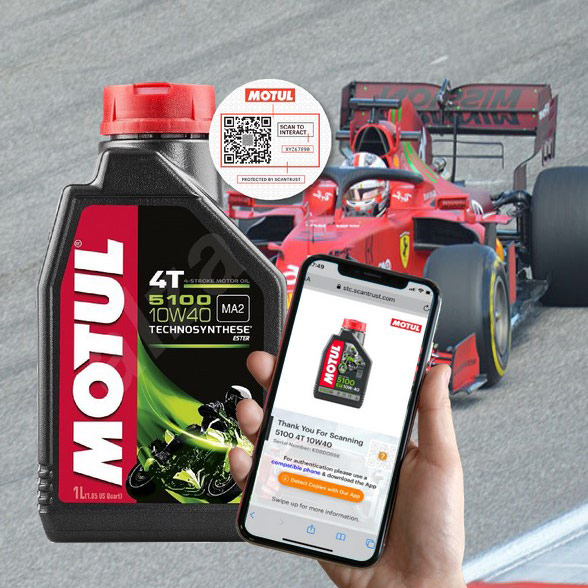

See case study
How do you implement serialized QR codes in a production line?
Implementing serialized QR codes in the manufacturing, production, or packing lines usually requires additional hardware implementation along with integration with an enterprise QR code generation and management software.
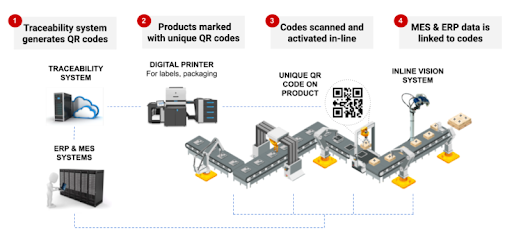
What printing hardware technology is suitable for printing serialized QR codes?
Not all printers can directly load or print serialized QR codes. Only printers and configurations that support variable data printing, such as digital printers, can print serialized (unique) codes on each label or package unit.
Analog or static printing technology which is commonly used for packaging, cartons, boxes, etc. doesn’t support variable data printing, which is necessary for serialized or unique code printing. One option is hybrid printing – leveraging both digital and analog printing. This adds complexity, but many companies still choose this option to better meet their demands.
One other interesting option to note for serialized QR codes on product packaging is that QR codes can also be laser etched onto plastic and even metal surfaces. Lasering, as it’s known, is appealing for use cases on mechanical parts, such as in automotive or industrial applications, where wear and tear from usage would damage a printed or sticker-based QR code to the extent that it would not be readable for long.

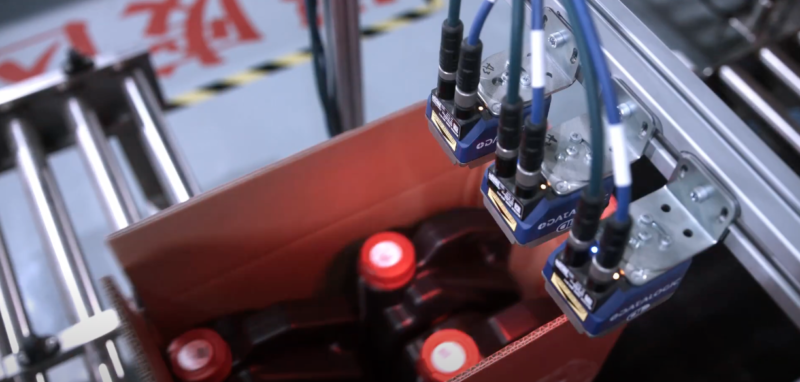
How are serialized QR codes scanned and activated in the production line?
Inline scanning systems are made up of a specialized scanner connected to a local server and placed on the packaging line or line management system. Data from this scanning system is buffered on the local server and then synchronized with the MRP, ERP and/or traceability system.

Key considerations that impact the selection and implementation of an inline scanning system include:
- Line speed
- Environmental (lighting)
- Product shape and code distortion
- Code location (is it fixed or variable)
- Field of view, variability in product position on the line
- Whether or not multiple products being scanned at or individually
Inline scanning system providers include Laetus, Datalogic, Cognex, and Lake Image. Scantrust has experience working with many such partners.
There are two main steps where inline scanning systems are used:
- Activation of codes – The scanning system “turns on” a code and ensures that each product is tracked from the moment it is produced, making it usable for traceability, anti-counterfeiting, customer engagement, etc. This is also important for billing-related reasons as code providers often price services based on volume of codes used. Many brands want to control code activation to prevent labels from being leaked to the market. This is especially important if product labels are supplied by a partner, as is often the case.
2. Aggregation and data association – Products are placed in boxes, crates, and pallets in the packaging line, and these logistic units themselves are labeled with different codes or identifiers, often with 1D barcodes. This process of association, or grouping products within logistical units, is called “aggregation”. Through system or scanning process integration, stakeholders downstream can scan the serialized QR codes on boxes, cases, or palettes as they enter and leave the warehouses and distribution centers. Thanks to aggregation, it’s possible to track the product in the supply chain based on the scans of the logistical unit they are contained in without having to scan the individual product itself.
What kinds of product data can be used with serialized QR codes?
Because serialized products are trackable at the unit-level, much more detailed and unit-associated information can be collected and retrieved than would be available with SKU-level codes. The below just represents a small variety of the kinds of data brands associate with serialized QR codes:
Supply chain data
- Upstream data on how that particular product was made
- What market(s) the product is destined for
- Which distributors are sending how many products where
- Where inventory is sitting, how fast it’s moving
- Where the product has been and who scanned it along the way
- Product batch
- Quality issues
Consumer data
- Demographic data of end-users
- Product authentication data
- Loyalty campaign scanning data
What are the benefits of serialized QR codes vs. RFID/ NFC
The three key reasons why QR codes are more popular for serialization are:
- They are more easily integrated into most product packaging
- Cost significantly less (capex and opex)
- Generate no electronic waste, unlike RFID
Considerations: Serialized QR codes for counterfeit detection
Counterfeit detection systems which rely on serialized codes are usually based on the premise that a consumer will only scan the product’s QR code once or twice, and if a single unique code is scanned many times, especially in disparate locations, it is likely counterfeit. These systems have shortfalls – you can learn more in our comparison of different QR code technologies for anti-counterfeiting.
Considerations: Serialized QR codes for GS1 Digital Link Integration
Serialized QR codes can comply with GS1 Digital Link standards by simply arranging their URL format according to the standard, including use of the Product Global Trade Item Number (GTIN). GS1 Digital Link enhances the functionality of serialized QR codes by connecting them to product information and resources online in a standardized way. Your QR code solution provider should provide this compatibility.
Conclusion: Serialized QR codes provide wide benefits, but also some complexity
Regulatory changes and decreasing implementation costs have accelerated the shift toward use of serialized QR codes. Serialized QR codes are already being used by many of the world’s top brands to unlock broad benefits to customers and their business, including for product and supply chain traceability, product authentication, and customer engagement. As Digital Product Passports gain traction, serialization will be increasingly required. Adopting the techniques and technologies listed here will become crucial for brands aiming to stay competitive, responsive to consumer needs, and compliant with the latest regulations. If you have questions or need a proposal for how to implement serialized QR codes with your company’s products, Scantrust is an excellent partner to bring the latest technology and deep expertise into your QR code serialization initiatives.